Could Trump’s bold vision for tariffs reshape the very foundation of U.S. trade—or destroy it?
What You Need to Know
🇺🇸 Persistent Tariffs in U.S. Policy:
- Despite political divides, there’s a consensus on tariffs; Biden has extended and introduced new tariffs set during Trump's administration.
🇨🇳 Focus on China:
- Trump's tariff plan targets Chinese imports to counteract US trade imbalances.
🏢 Role of Tariffs in Policy:
- Used for protection or revenue, fostering domestic growth and addressing trade imbalances.
🔍 Examples of Tariff Impact:
- U.S. steel tariffs initially raised prices but eventually boosted domestic production and lowered costs.
- The "chicken tax" helped American truck manufacturers by shielding them from competition.
🔙 Trump's Tariff Strategy:
- Aims to promote domestic production and economic resilience.
- Baseline tariffs and the Reciprocal Trade Act are central, focusing on reshoring and fair competition.
The Truth About Tariffs
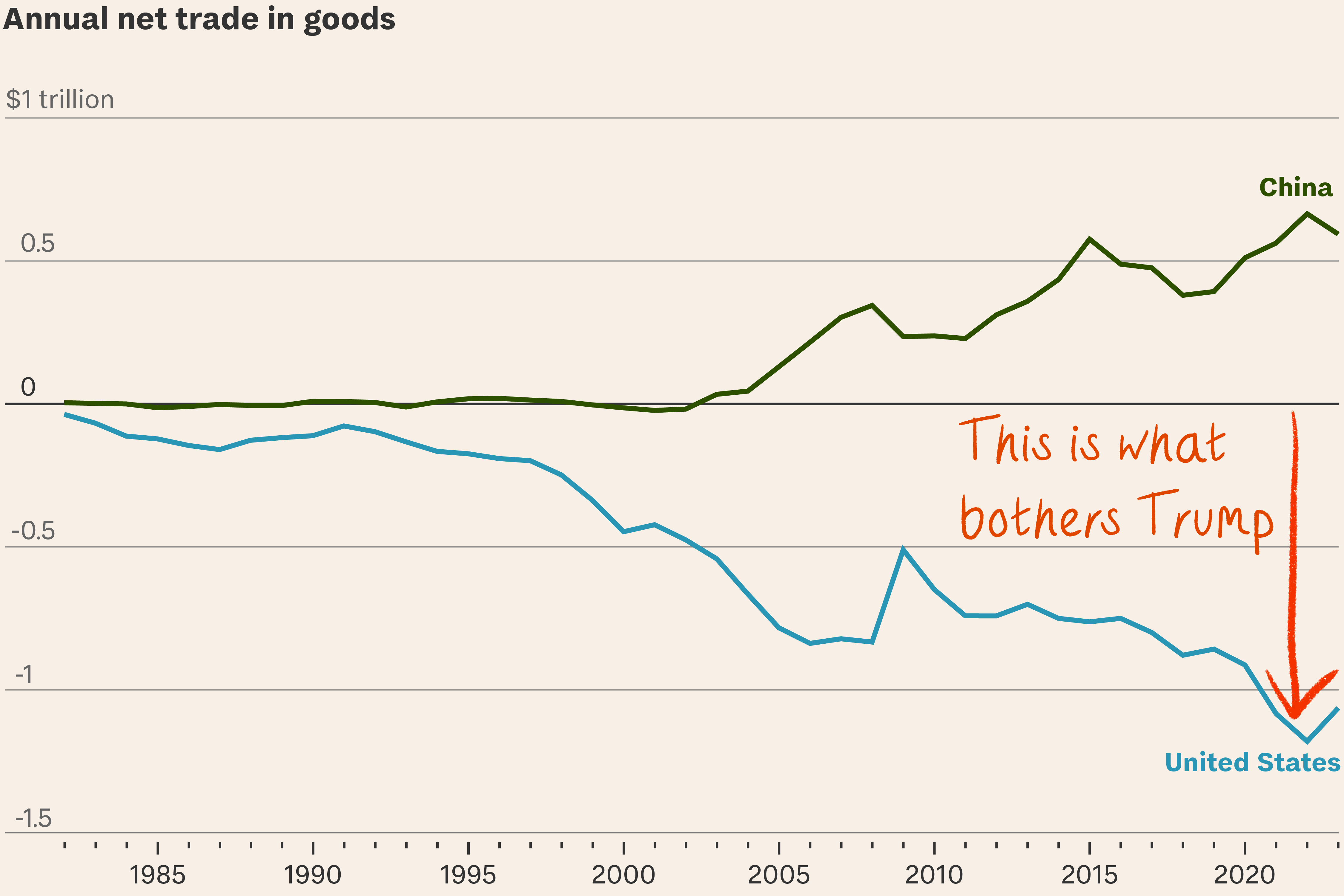
Both Trump and Biden administrations have leaned on tariffs, particularly in countering China’s trade practices. From revitalizing U.S. steel production to decades of success with the “chicken tax,” tariffs have shown their ability to shield key industries and promote growth.
But could Trump’s bold vision for tariffs reshape the very foundation of U.S. trade—or destroy it?
Tariffs And Their Role in Policy

A tariff is a tax placed on goods when they cross national borders. The most common type is an import tariff, which taxes goods brought into a country.
There are also export tariffs, which are taxes on goods a country exports, though these are rare. The United States does not allow export tariffs; the Constitution (Article I, Section 9) forbids them.
Tariffs are typically imposed for protection or revenue purposes. A protective tariff increases the price of imported goods relative to domestic goods, encouraging consumers to buy from local producers, who are thus “protected” from foreign competition.
The continuity of tariff policies across administrations, from President Trump to President Biden, reflects their enduring relevance.
For instance, the Biden administration has maintained many of Trump’s tariffs and introduced additional measures to protect emerging industries like green energy. These policies highlight the bipartisan recognition of tariffs as essential for bolstering domestic economic strength.
President William McKinley: The Tariff King

Trump often uses the McKinley 1890 administration as an example on the benefits of tariffs. McKinley formed the Blue Ribbon Committee’s for discussions on tariffs and currency reform, two defining issues of his presidency. President McKinley’s tariff policies were exemplified by the Dingley Tariff Act of 1897.
By funding the government through tariffs, McKinley avoided imposing direct federal income taxes on American households, allowing businesses and individuals to grow without the burden of federal income taxation—a system Trump has floated returning to.
After McKinley's assassination, progressives later pushed for the 16th Amendment in 1913 introducing the federal income tax in lieu of the tariff system that had sustained the nation without directly taxing citizens.
The shift to income taxes placed a new financial burden on individuals and businesses, diverging from McKinley’s vision of funding government through policies that strengthened American industry and protected workers.
Examples of Tariff Impact
Case Study: U.S. Steel Tariffs

President Trump’s tariffs on Chinese steel highlight the positive impact of strategic tariff policies. Initially criticized for driving up prices, these tariffs ultimately revitalized the U.S. steel industry. The short-term increase in prices was a necessary adjustment period that allowed domestic suppliers to scale up production. Once this transition occurred, steel prices stabilized at lower levels than before the tariffs, proving the long-term effectiveness of the policy.
This resurgence in domestic steel production not only saved American jobs but also reduced reliance on foreign suppliers. Industries that depend on steel, such as automotive and construction, benefited from a more resilient and cost-effective supply chain. The U.S. steel case underscores how tariffs can foster sustainable economic growth by encouraging domestic investment and production.
Case Study: The Chicken Tax

The 1964 “chicken tax” offers another example of tariffs’ success. Initially imposed as a retaliatory measure against European tariffs on U.S. broiler chickens by Germany, this 25% tariff on imported light European trucks shielded American manufacturers from foreign competition for decades.
The result was a thriving domestic truck market, with vehicles like the Ford F-150 becoming market leaders to this day.
This policy demonstrates that tariffs can provide the stability and protection needed for domestic industries to dominate both local and global markets.
Trump's Tariff Strategy

Trump’s trade strategy underscores a broader theme of economic sovereignty. The reliance on foreign-made goods, particularly from nations like China, has exposed vulnerabilities in supply chains and weakened domestic industries. Baseline tariffs and the Reciprocal Trade Act aim to reverse this trend by:
- Promoting Reshoring: Encouraging companies to bring production back to the U.S.
- Reducing Dependence on Adversaries: Strengthening domestic industries reduces reliance on imports from strategic competitors.
- Fostering Economic Resilience: A stronger domestic manufacturing base enhances the U.S.’s ability to weather global economic shocks.
Enact Baseline Tariffs
The plan proposes baseline tariffs on foreign-made goods, ensuring that imported products do not undercut domestic industries through unfair competition. By imposing a minimum tariff, the U.S. would:
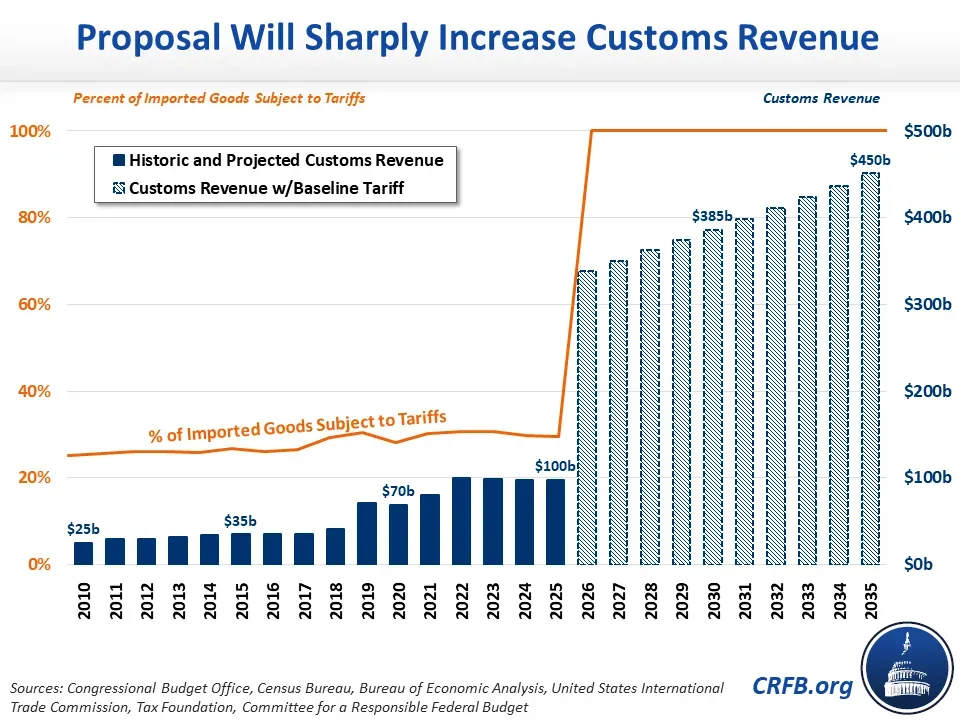
- Encourage Domestic Production: Baseline tariffs make foreign goods slightly more expensive, incentivizing consumers and businesses to buy American.
- Generate Revenue: Tariffs provide a new revenue stream that can offset other tax burdens.
- Deter Unfair Trade Practices: Countries engaging in dumping, subsidies, or other unfair practices face immediate consequences.
This policy aligns with the broader goal of reducing the tax burden on American workers, families, and businesses.
A Shift in Tax Policy
One of the most appealing aspects of Trump's plan is the idea of linking tariffs to domestic tax policy. As tariff revenues increase, taxes on American workers, families, and businesses can be reduced. This creates a virtuous cycle where:
- Foreign Producers Bear the Burden: Instead of relying solely on American taxpayers to fund government programs, tariffs shift some of this responsibility to foreign producers.
- Boosting Disposable Income: Lower taxes on individuals and businesses increase disposable income and stimulate economic growth.
- Strengthening Domestic Demand: With more money in their pockets, Americans are better positioned to support domestic industries.
This approach reframes tariffs not as a cost but as a tool for reducing domestic tax burdens and encouraging economic self-reliance.
The Reciprocal Trade Act
TheReciprocal Trade Act is another cornerstone of Trump's vision. This proposed legislation allows the U.S. to impose tariffs equal to those levied by other countries on American goods.
For example, if a country charges a 25% tariff on U.S. agricultural exports, the U.S. would reciprocate with a 25% tariff on imports from that country.
The benefits of this approach include:
- Eliminating Trade Disparities: Reciprocity ensures that U.S. goods are not disadvantaged in global markets.
- Strengthening Negotiating Power: The threat of reciprocal tariffs provides leverage in trade negotiations, encouraging other countries to lower their barriers.
- Promoting Fair Competition: Foreign producers are incentivized to compete on equal terms rather than relying on protectionist policies.
Respond to Unfair Trading Practices

The plan also emphasizes the importance of responding decisively to unfair trade practices such as dumping, intellectual property theft, and state subsidies. Tariffs are a key mechanism for addressing these issues, but they are part of a broader strategy that includes:
- Trade Agreements: Renegotiating deals to prioritize American interests.
- Targeted Measures: Imposing penalties on specific industries or countries engaging in unfair practices.
- Domestic Investments: Strengthening infrastructure and innovation to make U.S. industries more competitive globally.
By combining defensive measures (tariffs) with proactive investments, the plan seeks to ensure that the U.S. remains a leader in global trade while protecting its economic sovereignty.
Have you checked the market today? Check out Synvestable Live for premium news and coverage on over 10,000 tradable tickers. Register for FREE for in-depth coverage!